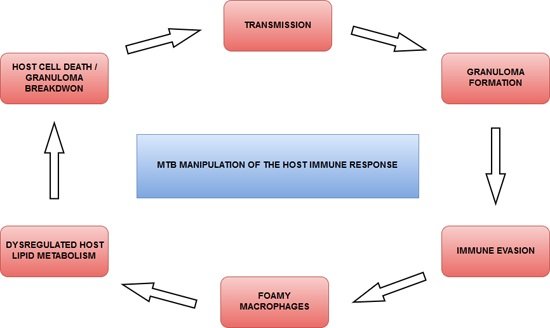
Model for caseum accumulation and granuloma progression.(a)
4.5 (782) · € 21.50 · En Stock
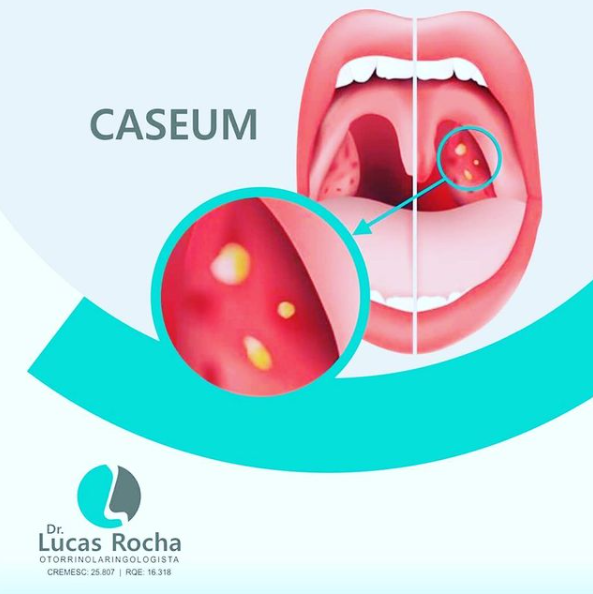
Download scientific diagram | Model for caseum accumulation and granuloma progression.(a) Intracellular Mtb synthesize and release cell wall components inside their host cell. These lipids accumulate in the internal vesicles in multivesicular bodies, which are exocytosed from the cell in vesicular form. (b) Because of the release of such vesicles, both infected and uninfected macrophages are exposed to cell wall mycolates and are induced to form foam cells. (c) The foam cells die by an inflammatory, necrotic process and release their lipid droplets into the extracellular milieu in the granuloma. (d) As a result of the fibrotic capsule, the human granuloma is an enclosed, isolated structure. The enclosed nature of the human granuloma leads to the accumulation of necrotic debris as caseum. We propose that this process is an integral part of the pathology that leads to active disease and transmission. from publication: Foamy macrophages and the progression of the human tuberculosis granuloma | The progression of tuberculosis from a latent, subclinical infection to active disease that culminates in the transmission of infectious bacilli is determined locally at the level of the granuloma. This progression takes place even in the face of a robust immune response | Granuloma, Macrophage and Tuberculosis | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Caseum: a Niche for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Drug-Tolerant Persisters

Diverse immune environments in human lung tuberculosis granulomas assessed by quantitative multiplexed immunofluorescence - Modern Pathology
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Extreme Drug Tolerance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Caseum

Microbial Offense vs Host Defense: Who Controls the TB Granuloma? - Amanda J. Martinot, 2018

Heterogeneity in tuberculosis pathology, microenvironments and therapeutic responses - Lenaerts - 2015 - Immunological Reviews - Wiley Online Library

A Novel Tool to Identify Bactericidal Compounds against Vulnerable Targets in Drug-Tolerant M. tuberculosis found in Caseum

The lipid environment of Mtb in caseous TB granulomas. Within foamy
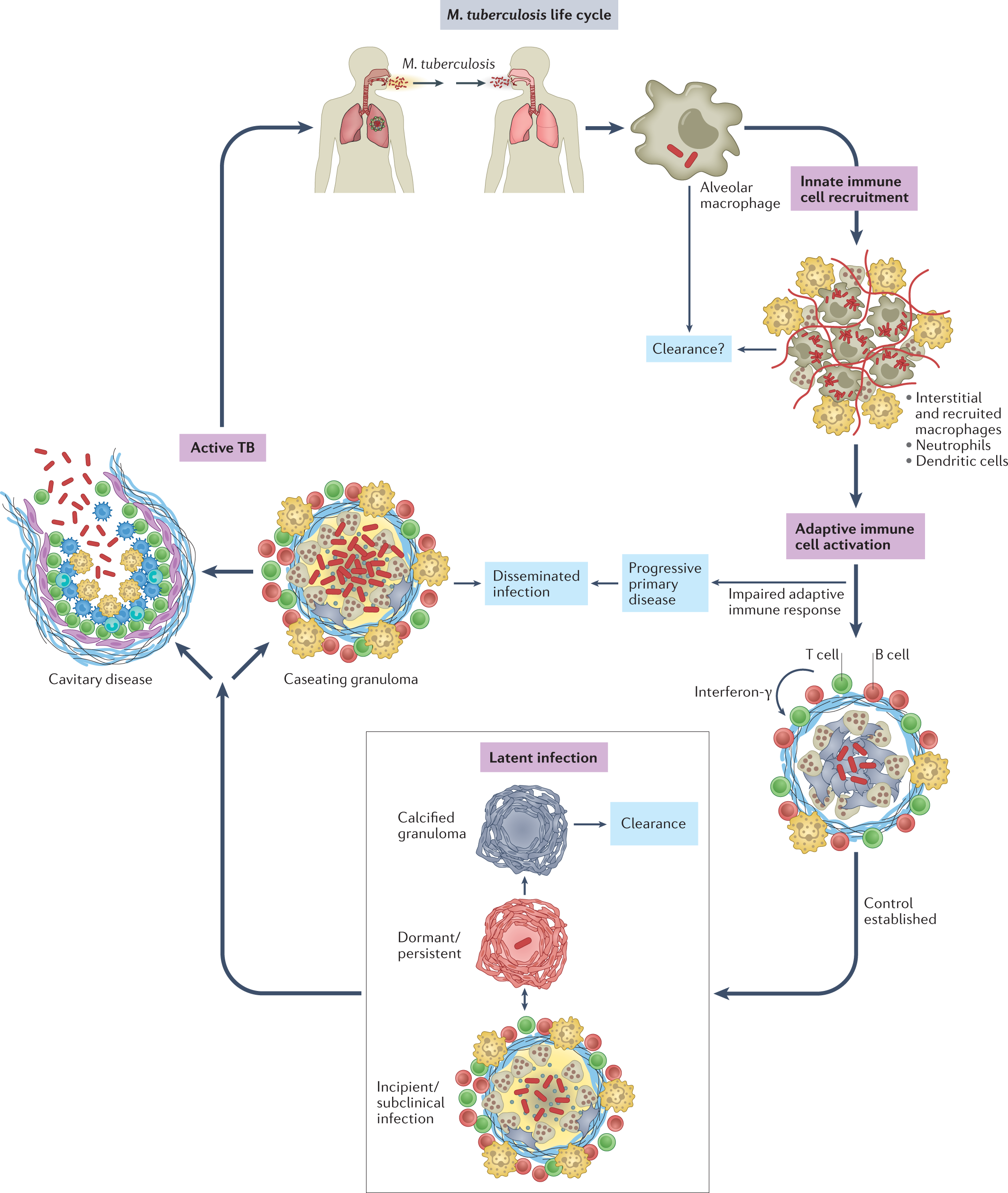
Immune evasion and provocation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis

Microbial Offense vs Host Defense: Who Controls the TB Granuloma? - Amanda J. Martinot, 2018
Comparing efficacies of moxifloxacin, levofloxacin and gatifloxacin in tuberculosis granulomas using a multi-scale systems pharmacology approach

Do chance encounters between heterogeneous cells shape the outcome of tuberculosis infections? - ScienceDirect

Thin-layer chromatographic analysis of lipids from the caseum and

Caseation of human tuberculosis granulomas correlates with elevated host lipid metabolism